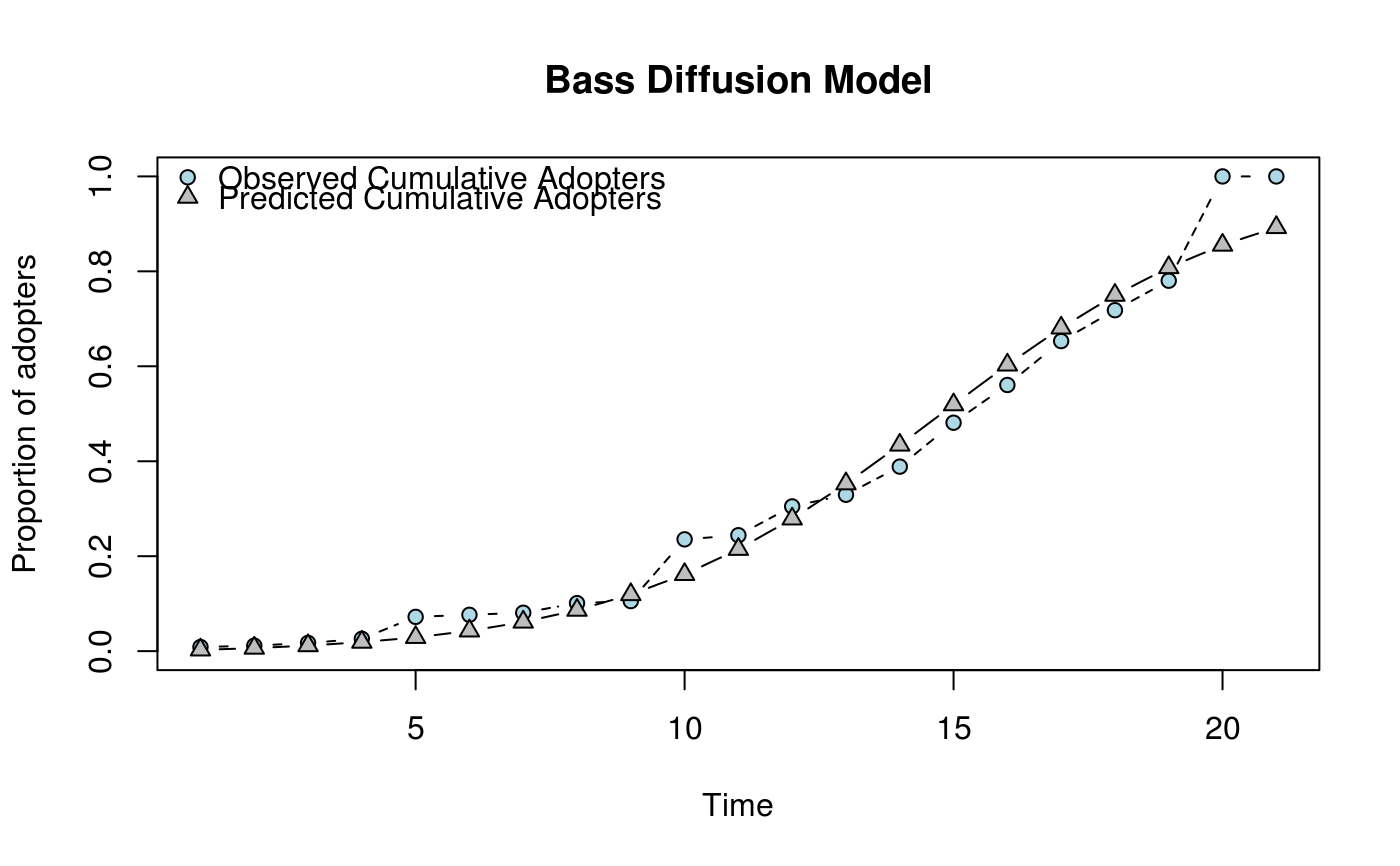
Fits the Bass Diffusion model. In particular, fits an observed curve of proportions of adopters to \(F(t)\), the proportion of adopters at time \(t\), finding the corresponding coefficients \(p\), Innovation rate, and \(q\), imitation rate.
fitbass(dat, ...)
# S3 method for class 'diffnet'
fitbass(dat, ...)
# Default S3 method
fitbass(dat, ...)
# S3 method for class 'diffnet_bass'
plot(
x,
y = 1:length(x$m$lhs()),
add = FALSE,
pch = c(21, 24),
main = "Bass Diffusion Model",
ylab = "Proportion of adopters",
xlab = "Time",
type = c("b", "b"),
lty = c(2, 1),
col = c("black", "black"),
bg = c("lightblue", "gray"),
include.legend = TRUE,
...
)
bass_F(Time, p, q)
bass_dF(p, q, Time)
bass_f(Time, p, q)Arguments
- dat
Either a diffnet object, or a numeric vector. Observed cumulative proportion of adopters.
- ...
Further arguments passed to the method.
- x
An object of class
diffnet_bass.- y
Integer vector. Time (label).
- add
Passed to
matplot.- pch
Passed to
matplot.- main
Passed to
matplot.- ylab
Character scalar. Label of the
yaxis.- xlab
Character scalar. Label of the
xaxis.- type
Passed to
matplot.- lty
Passed to
matplot.- col
Passed to
matplot.- bg
Passed to
matplot.- include.legend
Logical scalar. When
TRUE, draws a legend.- Time
Integer vector with values greater than 0. The \(t\) parameter.
- p
Numeric scalar. Coefficient of innovation.
- q
Numeric scalar. Coefficient of imitation.
Value
An object of class nls and diffnet_bass. For more
details, see nls in the stats package.
Details
The function fits the bass model with parameters \([p, q]\) for values \(t = 1, 2, \dots, T\), in particular, it fits the following function:
$$ F(t) = \frac{1 - \exp{-(p+q)t}}{1 + \frac{q}{p}\exp{-(p+q)t}} $$
Which is implemented in the bass_F function. The proportion of adopters
at time \(t\), \(f(t)\) is:
$$ f(t) = \left\{\begin{array}{ll} F(t), & t = 1 \\ F(t) - F(t-1), & t > 1 \end{array}\right. $$
and it's implemented in the bass_f function.
For testing purposes only, the gradient of \(F\) with respect to \(p\)
and \(q\) is implemented in bass_dF.
The estimation is done using nls.
References
Bass's Basement Institute Institute. The Bass Model. (2010). Available at: https://web.archive.org/web/20220331222618/http://www.bassbasement.org/BassModel/. (accessed live for the last time on March 29th, 2017.)
See also
Other statistics:
classify_adopters(),
cumulative_adopt_count(),
dgr(),
ego_variance(),
exposure(),
hazard_rate(),
infection(),
moran(),
struct_equiv(),
threshold(),
vertex_covariate_dist()
Examples
# Fitting the model for the Brazilian Farmers Data --------------------------
data(brfarmersDiffNet)
ans <- fitbass(brfarmersDiffNet)
# All the methods that work for the -nls- object work here
ans
#> Nonlinear regression model
#> model: dat ~ bass_F(Time, p, q)
#> data: parent.frame()
#> p q
#> 0.002279 0.336735
#> residual sum-of-squares: 0.05184
#>
#> Number of iterations to convergence: 10
#> Achieved convergence tolerance: 3.515e-06
summary(ans)
#>
#> Formula: dat ~ bass_F(Time, p, q)
#>
#> Parameters:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> p 0.0022787 0.0007245 3.145 0.00533 **
#> q 0.3367354 0.0268004 12.565 1.19e-10 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 0.05223 on 19 degrees of freedom
#>
#> Number of iterations to convergence: 10
#> Achieved convergence tolerance: 3.515e-06
#>
coef(ans)
#> p q
#> 0.002278742 0.336735353
vcov(ans)
#> p q
#> p 5.249307e-07 -1.888583e-05
#> q -1.888583e-05 7.182630e-04
# And the plot method returns both, fitted and observed curve
plot(ans)